NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Q1. A tall cylinder is filled with viscous oil. A round pebble is dropped from the top with zero initial velocity. From the plot shown in figure, indicate the one that represents the velocity (v) of the pebble as a function of time (t).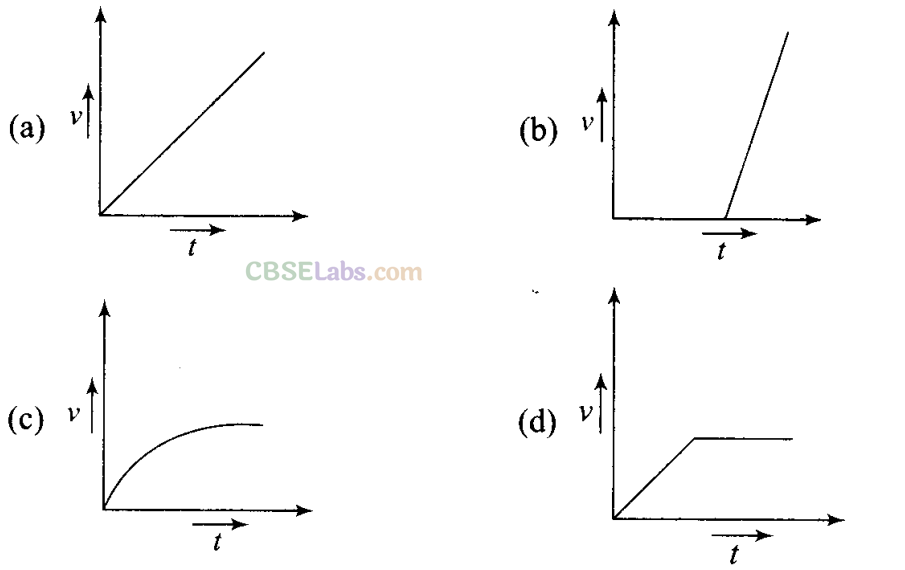
Sol: (c) In fluids, when the pebble is dropped from the top of a tall cylinder filled with viscous oil, a variable force called viscous force will act which increases with increase in speed. And at equilibrium this velocity becomes constant, that constant velocity is called terminal velocity.
When the pebble is falling through the viscous oil, the viscous force is F= 6πηrv
where r is the radius of the pebble, v is instantaneous speed, η is coefficient of viscosity. As the force is variable, hence acceleration is also variable so v-t graph will not be a straight line. First velocity increases and then becomes constant known as terminal velocity.
Q2. Which of the following diagrams does not represent a streamline flow?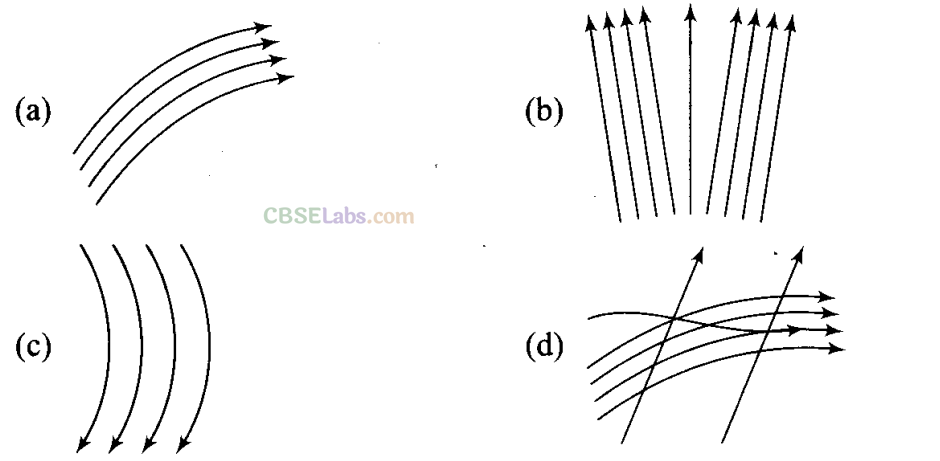
Sol. (d)
Streamline flow: Streamline flow of a liquid is that flow in which each element of the liquid passing through a point travels along the same path and with the same velocity as the preceding element passes through that point.
A streamline may be defined as the path, straight or curved, the tangent to which at any point gives the direction of the flow of liquid at that point.
The two streamlines cannot cross each other and the greater is the crowding of streamlines at a place, the greater is the velocity of liquid particles at that place. If we consider a cross¬sectional area, then a point on the area cannot have different velocities at the same time
Path ABC is streamline as shown in the figure and v1, v2 and v3 are the velocities of the liquid particles at A, B and C point respectively.
Q3. Along a streamline,
(a) the velocity of a fluid particle remains constant
(b) the velocity of all fluid particles crossing a given position is constant
(c) the velocity of all fluid particles at a given instant is constant
(d) ' the speed of a fluid particle remains constant,
Sol:(b) As discussed above for a streamline flow of a liquid velocity of each particle at a particular cross-section is constant, because Av = constant (law of continuity) between two cross-section of a tube of flow. So we can say that along a streamline, the velocity of every fluid particle while crossing a given position is the same.
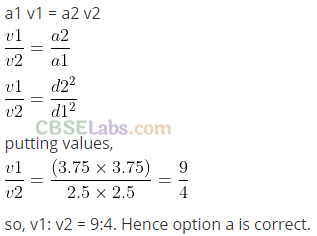
Q4. An ideal fluid flows through a pipe of circular cross-section made of two sections with diameters 2.5 cm and 3.75 cm. The ratio of the velocities in the two pipes is
(a) 9:4 (b) 3:2 (c)√3: √2 (d)√2:√3
Sol: (a) The situation is shown in the diagram below in which an ideal fluid is flowing through a pipe of circular cross sections.
Q5. The angle of contact at the interface of water-glass is 0°, ethylalcohol-glass is 0°, mercury-glass is 140° and methyliodide-glass is 30°. A glass capillary is put in a trough containing one of these four liquids. It is observed that the meniscus is convex. The liquid in the trough is
(a) water
(b) ethylalcohol
(c) mercury
(d) methyliodide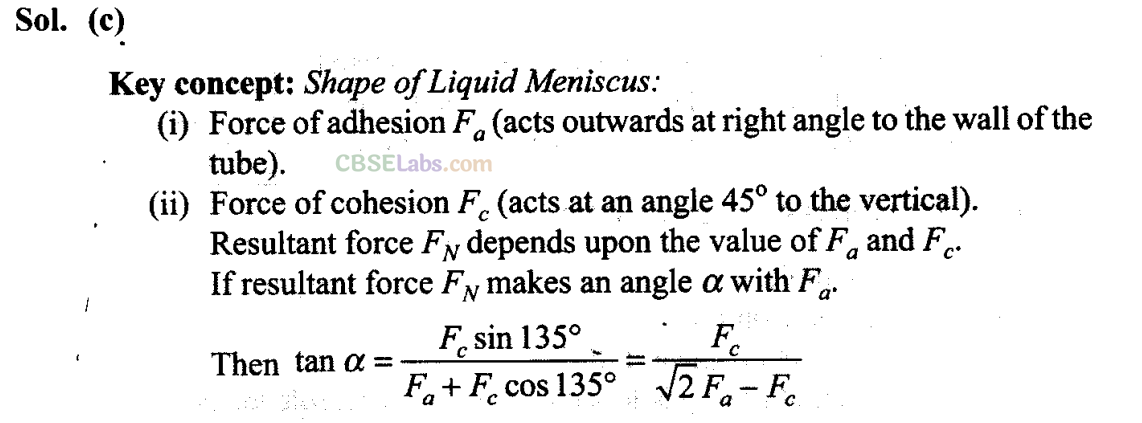

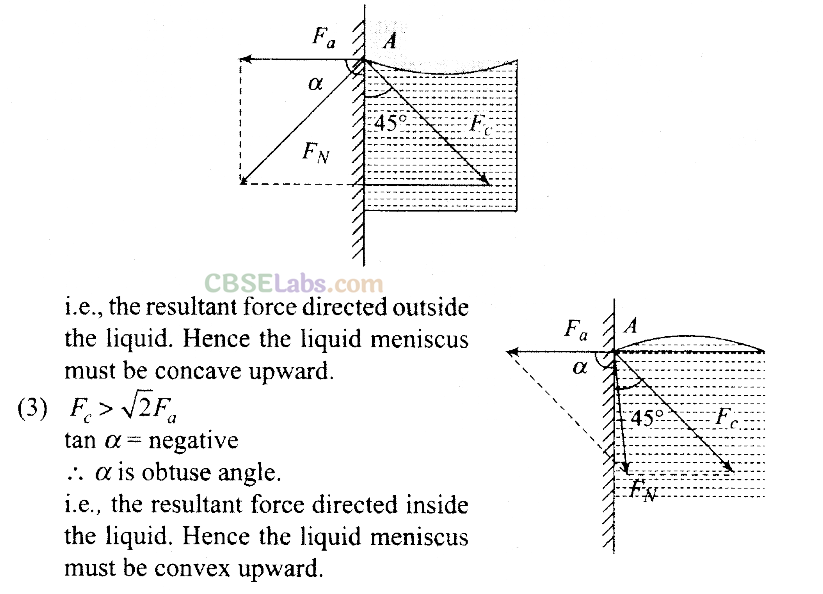
According to the question, the observed meniscus of liquid in a capillary tube is of convex upward which is only possible when angle of contact is obtuse. It is so when one end of glass capillary tube is immersed in a trough of mercury. Hence, the combination will be of mercury-glass (140°) as shown in the figure.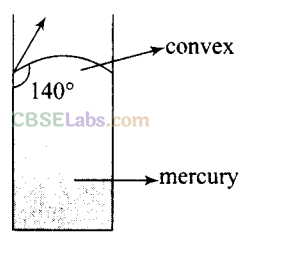
More Than One Correct Answer Type
Q6. For a surface molecule,
(a) the net force on it is zero
(b) there is a net downward force
(c) the potential energy is less than that of a molecule inside
(d) the potential energy is more than that of a molecule inside
Sol: (b, d)
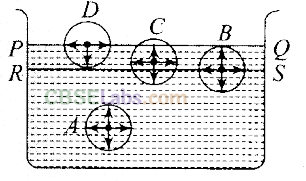
Key concept: To understand the concept of tension acting on the free
surface of a liquid, let us consider four liquid molecules like A, B, C and D. Their sphere of influence are shown in the figure.

😇 WHAT'S YOUR DOUBT DEAR ☕️
🌎 YOU'RE BEST 🏆