Our subject specific Class 7 Science Curiosity Worksheet and Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Heat Transfer in Nature Worksheet with Answers Pdf are aligned with latest patterns.
Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Heat Transfer in Nature Worksheet
Class 7 Heat Transfer in Nature Worksheet
Worksheet On Heat Transfer in Nature Class 7 – Heat Transfer in Nature Worksheet Class 7
A. Objective Type Questions
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Sanjay has to carry cold coffee to his friend’s home. Which of these will keep the coffee cold for the longest?

(a) X
(b) Y
(c) Z
(d) Both X and Z
Answer:
(a) X
Question 2.
A marble tile would feel cold as compared to a wooden tile on a winter morning, because the marble tile
(a) is a better conductor of heat than the wooden tile.
(b) is polished, while the wooden tile is not.
(c) reflects more heat than a wooden tile.
(d) is a poorer conductor of heat than the wooden tile.
Answer:
(a) is a better conductor of heat than the wooden tile.
Question 3.
Sunita lives in a place with very cold weather. She is getting her house painted. What colour should she choose for the roof surface of the house to keep it warm?
(a) White
(b) Blue
(c) Yellow
(d) Black
Answer:
(d) Black
![]()
Question 4.
Which process causes the air above the hot tea to get heated?
(a) Conduction
(b) Evaporation
(c) Radiation
(d) Convection
Answer:
(d) Convection
Question 5.
The given diagram shows different processes of heat transfer.
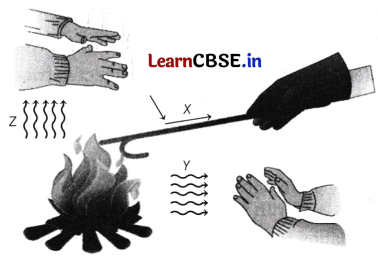
Choose the correct option.
(a) X-Convection, Y-Conduction, Z-Radiation
(b) X-Conduction, Y-Convection, Z-Radiation
(c) X-Conduction, Y-Radiation, Z-Convection
(d) X-Radiation, Y-Conduction, Z-Convection
Answer:
(c) X-Conduction, Y-Radiation, Z-Convection
Question 6.
Four different things are left under the Sun for half an hour. Which one gets the hottest?
(a) Plastic bottle
(b) Aluminium metal spoon
(c) Wooden block
(d) Glass jar
Answer:
(b) Aluminium metal spoon
Question 7.
The inner and outer surface of the flask is coated with plastic and steel. Why doesn’t heat appear at the outer surface of the flask if the flask contains hot liquid?
(a) Due to conduction between the inner and outer surfaces.
(b) Due to the insulation between the inner and outer surfaces.
(c) Due to radiation between the inner and outer surfaces.
(d) Due to convection between the inner and outer surfaces.
Answer:
(b) Due to the insulation between the inner and outer surfaces.
Question 8.
Bulbs of wax are stuck to the wooden rod as shown in the figure. Which of these will melt first?

(a) D
(b) E
(c) A
(d) B
Answer:
(b) E
Question 9.
Sushmita wants to eat bread and jam. The lid of the jam bottle would not come off. Which of these will work best?
(a) Put it in a bucket of ice.
(b) Pour hot water over it.
(c) Make a hole in the lid.
(d) Hammer it from all sides.
Answer:
(b) Pour hot water over it.
Question 10.
The process of transferring of heat without any contact between the source of heat and the heated object is called
(a) conduction
(b) convection
(c) radiation
(d) induction
Answer:
(c) radiation
![]()
Question 11.
A person prefers to sit by a fire during the cold winter months. Which of the following heat transfer types gives him the most heat?
(a) Convection and radiation together.
(b) Radiation will provide quick warmth.
(c) If it is near the fire, convection sounds good.
(d) Conduction from the fire.
Answer:
(b) Radiation will provide quick warmth.
Question 12.
In liquids and gases, heat transmission is primarily caused by
(a) Convection
(b) Radiation
(c) Conduction
(d) Conduction as well as convection
Answer:
(a) Convection
Question 13.
Petrol storage tanks are not painted black because
(a) black is a good absorber of radiation.
(b) black is a bad conductor of heat.
(c) black is a good conductor of heat.
(d) black is a bad emitter of radiation.
Answer:
(a) black is a good absorber of radiation.
Question 14.
Birds glide effortlessly in the air with the help of
(a) convection currents of air.
(b) Conduction of heat in the air.
(c) radiation of light through the atmosphere.
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) convection currents of air.
Question 15.
In which mode of heat transfer does the transfer of heat occur as a wave?
(a) Conduction
(b) Convection
(c) Radiation
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Radiation
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks by rearranging the words given with each sentence.
(a) In liquids and gases, heat is transferred mainly by the process of ___________ [covtenicon].
(b) The heat from the Sun reaches us by the process of ___________ [itnodiara].
(c) In a ___________ [ase] breeze, cool air from the sea moves towards the land.
(d) During the night, the land cools down faster than the sea. This causes a ___________ [dnal] breeze.
(e) Water from oceans, lakes, and rivers changes into water vapour during the process of ___________ [porevataoin].
Answer:
(a) Convection
(b) Radiation
(c) Sea
(d) Land
(e) Evaporation
![]()
Question 2.
Complete the blanks by choosing the appropriate words from the box given below.
(a) The process of water vapour changing into tiny droplets to form clouds is called ___________ [evaporation/condensation].
(b) The continuous movement of water between the earth and atmosphere is called the ___________ [water wheel/water cycle].
(c) In the afternoon, the land becomes warmer than the sea, and air moves from land to sea. This is called a ___________ [sea/land] breeze.
(d) In solids, heat is transferred from particle to particle mainly by ___________ [conduction/convection].
(e) Radiation does not need a ___________ [medium/tube] to transfer heat.
Answer:
(a) Condensation
(b) Water Cycle
(c) Land
(d) Conduction
(e) Medium
True/False
Put a (✓) with green sketch pen against the statements that are correct and a (✗) with red sketch pen against incorrect statements.
Question 1.
Riya made a few mistakes while writing some important points about the transfer of heat. Identify the incorrect statements and write them in their corrected form. Reward Riya by making a star against the correct statements.
(a) The land heats up faster than the sea during the day.
(b) Radiation is the mode of heat transfer that can occur through a vacuum.
(c) A frying pan becomes hot when kept on the flame due to convection.
(d) Land breezes occur during the day when cool air from the land moves towards the warmer sea.
(e) A black object acts as both a good absorber and a good emitter of heat.
(f) The water and air are poor conductors of heat.
Answer:
(a) T(✓)
(b) T(✓)
(c) F(✗)
(d) F(✗)
(e) T(✓)
(f) F(✗)
Question 2.
State whether the following statements are true or false, write T for true and F for false:
(a) Always rely on your sense of touch to determine whether an object is hot or cold.
(b) Light coloured clothes absorb more heat than dark coloured clothes.
(c) Heat always flows from a hotter object to a colder object.
(d) Heat can travel through a vacuum by the process of conduction.
(e) Sea breeze occurs during the daytime when land heats up faster than the sea.
(f) In a land breeze, warm air moves from the sea to the land at night.
Answer:
(a) F
(b) F
(c) T
(d) F
(e) T
(f) F
Match the Following
Question 1.
Match the Columns and choose the correct option given below:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Conduction | (i) Transfer of heat in solids |
| (b) Convection | (ii) Transfer of heat without a medium |
| (c) Radiation | (iii) Movement of heat in liquids and gases |
| (d) Sea breeze | (iv) Air moves from the sea to the land |
| (e) Land breeze | (v) Air moves from land to sea |
| (f) Evaporation | (vi) Water changes into vapour |
| (g) Condensation | (vii) Water vapour changes to droplets |
| (h) Water cycle | (viii) Continuous movement of water in nature |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Conduction | (i) Transfer of heat in solids |
| (b) Convection | (iii) Movement of heat in liquids and gases |
| (c) Radiation | (ii) Transfer of heat without a medium |
| (d) Sea breeze | (iv) Air moves from the sea to the land |
| (e) Land breeze | (v) Air moves from land to sea |
| (f) Evaporation | (vi) Water changes into vapour |
| (g) Condensation | (vii) Water vapour changes to droplets |
| (h) Water cycle | (viii) Continuous movement of water in nature |
Assertion-Reason Questions
The questions given below consist of an Assertion and a Reason. Based on that, choose the appropriate option.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the Reason is true.
Question 1.
Assertion: Heat is transferred in liquids by the process of convection.
Reason: Liquids allow heat to pass through them easily by conduction.
Answer:
(c) The assertion is true because in liquids, heat is mainly transferred through convection. When a liquid is heated, the particles at the bottom become warm, rise, and the cooler particles move down to take their place. This movement creates a convection current that helps spread heat through the liquid. The reason is false because liquids do not pass heat easily through conduction like solids do. So, the correct explanation is that heat in liquids is mostly transferred by convection, not conduction.
Question 2.
Assertion: Sea breeze occurs during the day.
Reason: Land heats up faster than water during the day.
Answer:
(a) During the day, the land heats up faster than the sea. The warm air above the land rises, and the cooler air from the sea moves in to take its place. This movement of cool air from the sea to the land is called a sea breeze. So, the sea breeze happens because the land gets hotter than the water during the day.
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion: Radiation can occur even in a vacuum.
Reason: Radiation does not require any medium for heat transfer.
Answer:
(a) Radiation is a way of heat transfer that can happen without any medium, like air or water. That’s why heat from the Sun reaches the Earth through the vacuum of space. Since radiation does not need any medium, it can occur in a vacuum.
Question 4.
Assertion: Sea breeze helps cool coastal areas during the day.
Reason: Water heats up more slowly than land during the day.
Answer:
(a) In solids, particles are closely packed, so they transfer heat to each other quickly through conduction, making it the main method of heat transfer in solids.
Question 5.
Assertion: Clouds form due to condensation.
Reason: Water vapour cools and changes into tiny droplets of water.
Answer:
(a) Clouds form when water vapour in the air cools and condenses into tiny droplets of water. This process of condensation happens when the air reaches a certain temperature, allowing water vapour to change back into liquid form, forming clouds.
Case-Based Questions
Read the given case study carefully and answer the questions that follow:
Raksha conducted an activity, and she kept four boxes containing equal-sized butter cubes under the sun. The boxes were of the same shape and size but made of different materials. Raksha then noted how long the butter cubes in each box took to melt.
| Box | Time taken by the butter cubes to melt |
| Box-1 | 12 minutes |
| Box-2 | 17 minutes |
| Box-3 | 6 minutes |
| Box-4 | 8 minutes |
Question 1.
Which box is the best conductor of heat?
(a) Box-1
(b) Box-4
(c) Box-3
(d) Box-2
Answer:
(c) Box-3
Question 2.
Which box is the worst conductor (insulator) of heat?
(a) Box-4
(b) Box-3
(c) Box-2
(d) Box-1
Answer:
(d) Box-1
Question 3.
Raksha repeated the same activity with each box wrapped in a woolen cloth. Which of the following is likely to have happened?
(a) The butter cubes in the boxes would have melted faster.
(b) The butter cubes in the boxes would not have melted.
(c) The butter cubes in each box would have taken longer to melt.
(d) The butter cubes in the boxes would have melted at the same time as before.
Answer:
(c) The butter cubes in each box would have taken longer to melt.
B. Subjective Type Questions
Define the following terms
Question 1.
Heat
___________________________________________________
Question 2.
Radiation
___________________________________________________
Question 3.
Convection
___________________________________________________
Question 4.
Sea breeze
___________________________________________________
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Shopkeepers selling ice blocks usually cover them with jute sacks. Explain why?
___________________________________________________
Question 2.
Birds puff up their feathers in winter. Why?
___________________________________________________
![]()
Question 3.
To keep her soup warm, Ritu wrapped the container in which it was kept with a woollen cloth. Can she apply the same method to keep a glass of cold drink cool? Give a reason for your answer.
___________________________________________________
Question 4.
How does heat travel in air? In which direction does smoke go?
___________________________________________________
Question 5.
Explain why heat transfer through convection is not possible in solids.
___________________________________________________
Question 6.
Study the diagram carefully and name the process by which transfer of heat is taking place.

___________________________________________________
Question 7.
Why does a metal spoon feel colder than a wooden spoon when both are at the same temperature?
___________________________________________________
Question 8.
During the day, why does the air near the sea feel cooler than the air on land?
___________________________________________________
Question 9.
Why do coastal areas experience a breeze blowing from the sea during the night and from the land during the day?
___________________________________________________
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Is it possible to construct buildings that are not affected much by heat and cold outside? Justify your answer.
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Question 2.
Briefly explain why a mud house with the shed roofs keeps cool in summer.
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Question 3.
The water and air are poor conductors of heat. Then, how does the heat transfer take place in these substances?
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Question 4.
Study the given figure carefully and answer the following questions.

(a) What are the names of the two types of breezes shown in the figures?
(b) Explain how each of these breezes occurs.
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Question 5.
Why do cooks prefer using metal pans with plastic or wooden handles? Explain using the concept of heat transfer.
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Question 6.
In some coastal villages, houses are built with large windows facing the sea. How might this design help during hot summer afternoons? Explain the reason behind it.
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Question 7.
After a sunny day, the puddles on the road dry up. Explain how heat plays a role in this process and mention which part of the water cycle this represents.
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
![]()
Question 8.
A woolen blanket keeps us warm even though it does not produce heat. Why does this happen? Relate it.
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Question 9.
Observe the diagram below showing air movement near the sea during the day. Label the warm air and cool air regions. Also, explain which type of breeze is shown and why it occurs.

___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Ram and Arjun live in a hostel in two different rooms. AC is fitted near the ceiling in Ram’s room, while in Arjun’s room, it is fitted beside his study table near the floor. Arjun says that the position of his AC is appropriate, and it cools the room in a better manner as compared to Ram’s room. Is he correct? If not, give a reason.
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Question 2.
At a campsite, there are tents of two shades, one made with black fabric and the other with white fabric. Which one will you prefer for resting on a hot summer afternoon? Give a reason for your choice. Would you prefer the same tent during winter?
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Question 3.
In a glass of hot boiling water, one end of each steel spoon, pencil, a plastic scale, and a paper straw is dipped. In which of these objects will the other end get hot? Explain in detail.
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Question 4.
Tina visited her grandparents who live near the sea. She felt cool winds blowing from the sea during the day, but warmer winds from the land during the night. One day, it rained heavily in the afternoon. Explain the science behind these observations using the concepts of heat transfer and the water cycle.
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Question 5.
During a school trip to a coastal village, students noticed that metal benches under the sun became hot quickly, while wooden benches remained cooler. At the same time, the weather was pleasant due to a breeze from the sea. Explain how the differences in materials and the direction of the breeze are related to heat transfer. Also, describe how such weather can lead to rain.
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Skill-Based Activities
Question 1.
Complete the following words with the help of the hints:
(a) C __ __ __ U __ __ __ R
Hint: A material that allows heat to pass through it.
(b) L __ __ D __ __ E __ __ E
Hint: Movement of cooler air from the land towards the sea.
(c) C __ __ DU __ __ IO __
Hint: The process of heat transfer through liquids and gases.
(d) INF __ __ __ RATI __ __
Hint: The process of water seeping into the ground.
Question 2.
Observe the given diagram and answer the questions that follow. Water is being boiled in a wide-based an of wide base.

(a) Which position, P or T, will feel warmer?
___________________________________________________
(b) Fill up the boxes P and T to indicate the mode of flow of heat to the hand.
___________________________________________________
![]()
Question 3.
Identify the incorrect word in each sentence and rewrite the following sentences in their corrected form.
(a) Cotton fabric is a good conductor of heat.
___________________________________________________
(b) Solar panels harness wind energy to produce electricity.
___________________________________________________
(c) Heat energy can be transferred through conduction, convection, or evaporation.
___________________________________________________
Question 4.
Choose the odd one out and justify your choice.
(a) Conduction, Thermometer, Radiation, Convection
___________________________________________________
(b) Hot utensil, Land breeze, Hair dryer, Sea breeze
___________________________________________________
(c) Wood, Plastic, Glass, Copper
___________________________________________________
(d) Conduction, Radiation, Convection, Air
___________________________________________________
The post Heat Transfer in Nature Class 7 Worksheet with Answers Science Chapter 7 appeared first on Learn CBSE.
📚 NCsolve - Your Global Education Partner 🌍
Empowering Students with AI-Driven Learning Solutions
Welcome to NCsolve — your trusted educational platform designed to support students worldwide. Whether you're preparing for Class 10, Class 11, or Class 12, NCsolve offers a wide range of learning resources powered by AI Education.
Our platform is committed to providing detailed solutions, effective study techniques, and reliable content to help you achieve academic success. With our AI-driven tools, you can now access personalized study guides, practice tests, and interactive learning experiences from anywhere in the world.
🔎 Why Choose NCsolve?
At NCsolve, we believe in smart learning. Our platform offers:
- ✅ AI-powered solutions for faster and accurate learning.
- ✅ Step-by-step NCERT Solutions for all subjects.
- ✅ Access to Sample Papers and Previous Year Questions.
- ✅ Detailed explanations to strengthen your concepts.
- ✅ Regular updates on exams, syllabus changes, and study tips.
- ✅ Support for students worldwide with multi-language content.
🌐 Explore Our Websites:
🔹 ncsolve.blogspot.com
🔹 ncsolve-global.blogspot.com
🔹 edu-ai.blogspot.com
📲 Connect With Us:
👍 Facebook: NCsolve
📧 Email: ncsolve@yopmail.com

😇 WHAT'S YOUR DOUBT DEAR ☕️
🌎 YOU'RE BEST 🏆